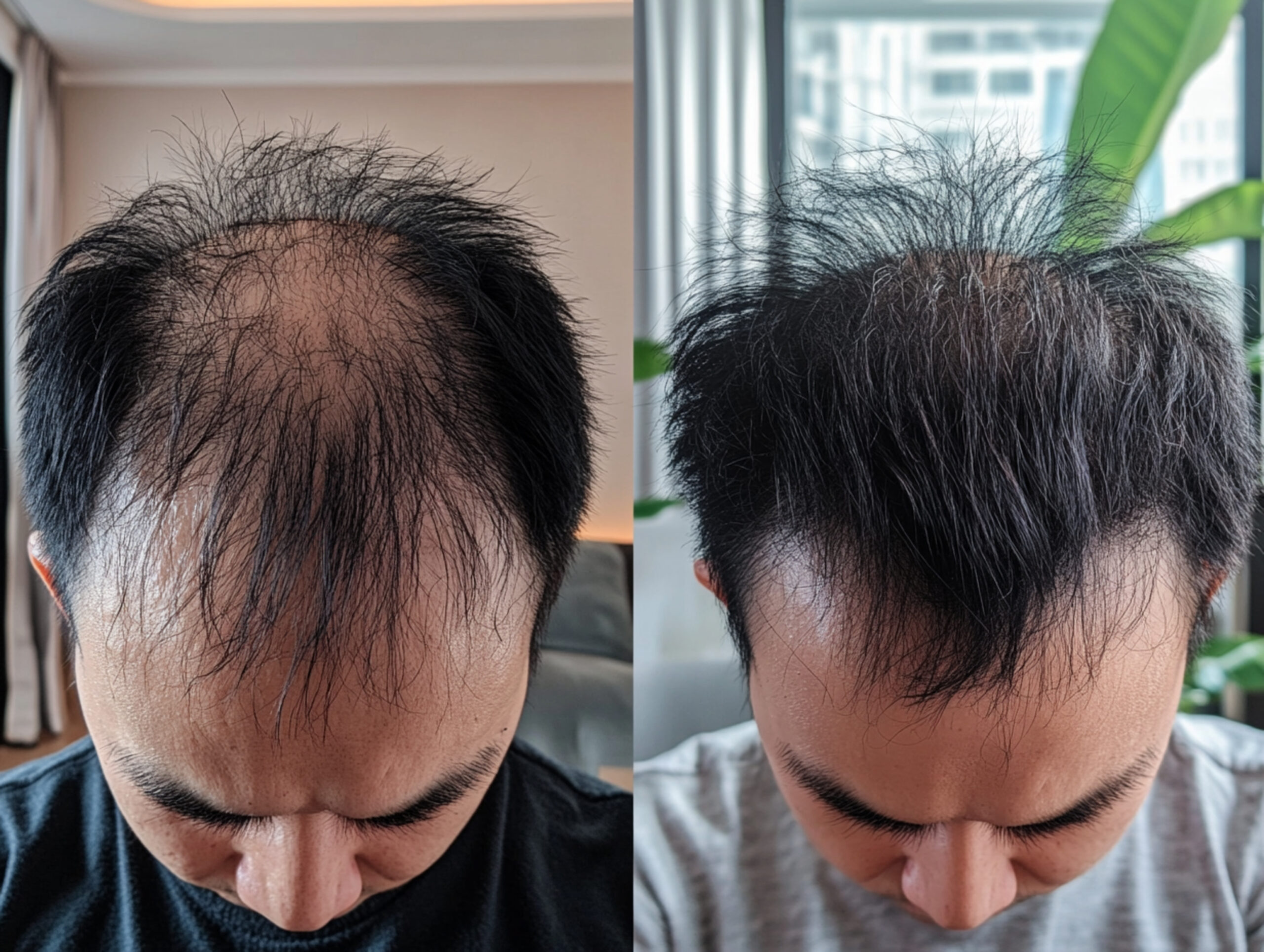
Hair loss is a common concern that affects millions of people worldwide across age, gender, and ethnicity. While losing some hair daily is normal, noticeable or progressive hair loss often signals an underlying condition. Two of the most commonly confused types are Alopecia Areata and Androgenic Alopecia. Although both lead to hair loss, their causes, patterns, progression, and treatment approaches are very different. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
At CCube Homoeopathy, under the guidance of Dr. Rashmi Chandwani, hair loss conditions such as Alopecia Areata and Androgenic Alopecia are approached with a strong focus on individualized and holistic care. Dr. Rashmi Chandwani emphasizes accurate diagnosis, understanding the root cause of hair loss, and tailoring treatment according to each patient’s physical, emotional, and lifestyle factors
What Is Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles. This disrupts the normal hair growth cycle and leads to sudden hair loss.
Key Features of Alopecia Areata
- Sudden onset of hair loss
- Well-defined, round or oval bald patches
- Can affect the scalp, eyebrows, beard, eyelashes, or body hair
- Hair follicles remain alive, so regrowth is possible
- Alopecia Areata can occur at any age, including childhood, and affects men and women equally
Types of Alopecia Areata
- Patchy Alopecia Areata: Localized bald patches on the scalp
- Alopecia Totalis: Complete loss of scalp hair
- Alopecia Universalis: Loss of all body hair
What Is Androgenic Alopecia?
Androgenic Alopecia commonly known as male pattern baldness or female pattern hair loss is a genetically determined condition influenced by hormones, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Key Features of Androgenic Alopecia
- Gradual thinning of hair
- Predictable pattern of hair loss
- Progressive shrinkage of hair follicles
- Usually permanent without treatment
Unlike Alopecia Areata, Androgenic Alopecia does not involve immune dysfunction and does not occur suddenly.
Patterns of Hair Loss: A Major Difference
Alopecia Areata Pattern
- Sudden appearance of smooth, bald patches
- Hair loss may occur overnight or within days
- Surrounding hair usually appears normal
- “Exclamation mark” hairs may be seen at patch edges
Androgenic Alopecia Pattern
- Men: Receding hairline and thinning at the crown
- Women: Diffuse thinning over the crown with a preserved frontal hairline
- Slow progression over months or years
- These distinct patterns often help clinicians differentiate between the two conditions
Causes: Autoimmune vs Hormonal
Causes of Alopecia Areata
- Autoimmune attack on hair follicles
- Genetic predisposition
- Triggers such as stress, infections, or emotional trauma
- Association with autoimmune conditions like thyroid disorders, vitiligo, or diabetes
Causes of Androgenic Alopecia
- Genetic sensitivity of hair follicles to DHT
- Hormonal influence
- Aging
- Strong family history
In simple terms, Alopecia Areata is immune-driven, while Androgenic Alopecia is hormone and genetics driven.
Progression and Prognosis
Alopecia Areata
- Highly unpredictable
- Hair may regrow completely, partially, or not at all
- Relapses are common
- Early intervention improves outcomes
Androgenic Alopecia
- Gradual and progressive
- Hair thinning worsens if untreated
- Advanced follicle miniaturization limits regrowth
Diagnosis: How Are They Identified?
Accurate diagnosis includes:
- Detailed medical and family history
- Clinical scalp and hair examination
- Dermoscopy (trichoscopy)
- Blood tests if autoimmune disease is suspected
- In Alopecia Areata, the scalp appears smooth and non-scarred, while in Androgenic Alopecia, follicular miniaturization is clearly visible.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Both conditions can significantly affect emotional well-being. Alopecia Areata often causes sudden emotional distress due to its abrupt and visible nature, leading to anxiety, depression, or social withdrawal. Androgenic Alopecia may gradually affect confidence, especially in younger individuals and women, where hair is closely tied to identity. Addressing emotional health is an essential part of holistic care.
Treatment Approaches: Why They Differ
Because the root causes are different, treatment strategies are also different.
Managing Alopecia Areata
- Focus on regulating immune response
- Stress management plays a key role
- Treatment is highly individualized
Managing Androgenic Alopecia
- Aim to slow progression and preserve existing hair
- Long-term management is often required
- Best results occur when treatment begins early
- A one-size-fits-all approach is ineffective for both conditions.
FAQs
Can Both Conditions Occur Together?
Yes. Though uncommon, a person can have both Alopecia Areata and Androgenic Alopecia simultaneously. In such cases, precise diagnosis is essential to manage each condition appropriately.
Is Androgenic Alopecia the same as Alopecia Areata?
No, androgenic alopecia and alopecia areata are not the same. Androgenic alopecia is a genetically and hormonally driven condition caused by the effect of androgens on hair follicles, leading to gradual thinning of hair in a characteristic pattern. In contrast, alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks hair follicles, causing sudden patchy hair loss. The causes, pattern of hair loss, and treatment approaches are completely different in both conditions.
How is alopecia treated in toddlers?
Treatment of alopecia in toddlers depends on identifying the underlying cause. Common reasons include nutritional deficiencies, fungal infections, alopecia areata, or frictional hair loss. A detailed clinical evaluation is essential before starting treatment. Management usually focuses on correcting deficiencies, treating infections if present, ensuring gentle hair care, and supporting natural hair regrowth. In most toddlers, hair loss is temporary and reversible once the root cause is addressed.
What is the difference between Androgenic Alopecia and Diffuse Alopecia Areata?
Androgenic alopecia is a slow, progressive form of hair loss that follows a specific pattern and is influenced by genetics and hormones. Alopecia areata, however, presents as sudden and widespread hair loss over the scalp without clearly defined bald patches. While androgenic alopecia progresses gradually, diffuse alopecia areata may show rapid onset and has an autoimmune basis.
What are the different types of Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia areata can present in several forms. The most common type is patchy alopecia areata, where round or oval bald patches appear on the scalp. In more severe forms, it may progress to alopecia totalis, which involves complete loss of scalp hair, or alopecia universalis, where there is loss of hair from the entire body. Another variant is ophiasis, characterized by hair loss along the margins of the scalp, especially the occipital and temporal regions.
What is the difference between Androgenic Alopecia and Telogen Effluvium?
Androgenic alopecia is a chronic and progressive condition that leads to gradual thinning of hair due to genetic and hormonal factors. Telogen effluvium, on the other hand, is an acute and temporary condition caused by physical or emotional stress, illness, childbirth, surgery, or nutritional deficiencies. Hair fall in telogen effluvium is sudden and diffuse but usually reversible once the triggering factor is corrected.
Importance of Personalized Care
Hair loss is not merely a cosmetic concern—it often reflects deeper systemic, hormonal, or emotional imbalances. Correct identification of the type of alopecia is critical before starting treatment. Misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective therapy and frustration.
Personalized care considers:
- Type and stage of alopecia
- Age and gender
- Lifestyle and emotional factors
- Overall health and associated conditions
CCube Homoeopathy-a pioneer in hairfall care
At Ccube Homoeopathy, under the guidance of Dr. Rashmi Chadwani, alopecia is approached with a clear understanding that alopecia areata and androgenic alopecia are fundamentally different conditions and therefore require individualized care. Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder characterized by sudden, patchy hair loss in well-defined round or oval areas on the scalp or other parts of the body, often triggered by stress, emotional disturbances, or immune imbalance.
Since the hair follicles are not permanently damaged, timely and personalized homoeopathic treatment aims to restore immune balance and stimulate natural hair regrowth by addressing the patient’s physical, emotional, and mental state. In contrast, androgenic alopecia is a genetically and hormonally influenced condition that develops gradually, presenting as patterned thinning of hair receding hairline and crown thinning in men, and diffuse crown thinning in women.
At Ccube Homoeopathy, Dr. Rashmi Chadwani emphasizes a constitutional homoeopathic approach for androgenic alopecia, focusing on slowing progression, strengthening weakened hair follicles, improving scalp health, and correcting internal imbalances rather than offering temporary cosmetic solutions. By treating the individual as a whole rather than just the hair loss, homoeopathy at Ccube Homoeopathy strives for sustainable, long-term improvement in both conditions.
Final Thoughts
While Alopecia Areata and Androgenic Alopecia both result in hair loss, they are fundamentally different conditions. Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disorder marked by sudden, patchy hair loss and unpredictable recovery. Androgenic Alopecia is a genetically and hormonally driven condition characterized by gradual, progressive thinning. Understanding these differences empowers individuals to seek timely, targeted, and effective care. Early diagnosis and a holistic approach can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life.
If you or someone you know is experiencing hair loss, consulting a qualified healthcare professional for proper evaluation is the most important first step. At CCube Homoeopathy, the goal is not only to address visible hair loss but also to support overall health, immune balance, and long-term well-being, helping patients manage alopecia more effectively and confidently through personalized homoeopathic care.